Recently, UNESCO designates 11 new biosphere reserves around the world . Due to this move UNESCO has protected natural habitats and promote sustainable development for us. Biosphere reserves are areas of terrestrial and coastal ecosystems which is act like our lungs. They balance the conservation of biodiversity with human activities. Let’s take a closer look at these new biosphere reserves and understand their significance.
What is a Biosphere Reserve?
UNESCO Designates 11 New Biosphere Reserves but A biosphere reserve is a designated area that combines conservation and sustainable use. These areas are meant to preserve the diversity of species, ecosystems, and landscapes. They also provide opportunities for research and education. UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere (MAB) program oversees these reserves.
The Purpose of Biosphere Reserves
UNESCO Designates 11 New Biosphere Reserves and Biosphere reserves serve multiple purposes:
- Conservation: Protecting genetic resources, species, and ecosystems.
- Development: Fostering sustainable economic and human development.
- Logistics: Supporting research, monitoring, education, and information exchange.
UNESCO Designates 11 New Biosphere Reserves

Sure, here’s a table with the reordered biosphere reserves:
| Sr. | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Kempen-Broek Transboundary Biosphere Reserve (Belgium, Kingdom of the Netherlands) |
| 2 | Darién Norte Chocoano Biosphere Reserve (Colombia) |
| 3 | Madre de las Aguas Biosphere Reserve (Dominican Republic) |
| 4 | Niumi Biosphere Reserve (Gambia) |
| 5 | Colli Euganei Biosphere Reserve (Italy) |
| 6 | Julian Alps Transboundary Biosphere Reserve (Italy, Slovenia) |
| 7 | Khar Us Lake Biosphere Reserve (Mongolia) |
| 8 | Apayaos Biosphere Reserve (Philippines) |
| 9 | Changnyeong Biosphere Reserve (Republic of Korea) |
| 10 | Val d’Aran Biosphere Reserve (Spain) |
| 11 | Irati Biosphere Reserve (Spain) |
Here i am describing 11 UNESCO Designates 11 New Biosphere Reserves in detail-
1. Kempen-Broek Transboundary Biosphere Reserve (Belgium, Kingdom of the Netherlands)
The Kempen-Broek Transboundary Biosphere Reserve spans the border between Belgium and the Kingdom of the Netherlands. This area is characterized by a mix of wetlands, forests, and heathlands. The landscape is diverse, featuring unique flora and fauna. Conservation efforts in this region focus on maintaining biodiversity and promoting sustainable land use practices. The local communities engage in eco-friendly agriculture and tourism.
2. Darién Norte Chocoano Biosphere Reserve (Colombia)
The Darién Norte Chocoano Biosphere Reserve is located in the northwestern part of Colombia. It encompasses a portion of the Darién Gap, a dense jungle that forms the bridge between Central and South America. This area is known for its rich biodiversity, including numerous endemic species. The reserve also supports indigenous communities who rely on traditional practices for their livelihoods. Conservation initiatives aim to protect the unique ecosystems and cultural heritage of the region.
3. Madre de las Aguas Biosphere Reserve (Dominican Republic)
Madre de las Aguas Biosphere Reserve, located in the Dominican Republic, is renowned for its mountainous terrain and diverse ecosystems. The reserve includes cloud forests, rivers, and wetlands that are home to a variety of plant and animal species. Efforts here focus on water conservation, as the area is crucial for the island’s freshwater supply. Sustainable tourism and community involvement are key aspects of the management strategy.
4. Niumi Biosphere Reserve (Gambia)
The Niumi Biosphere Reserve is situated in the northern region of Gambia. This area includes coastal mangroves, wetlands, and savannahs, providing habitats for a wide range of wildlife, including migratory birds and marine species. The reserve supports sustainable fishing and farming practices, helping local communities to maintain their traditional lifestyles while protecting natural resources.
5. Colli Euganei Biosphere Reserve (Italy)
Colli Euganei Biosphere Reserve is located in the Veneto region of Italy. It encompasses the Euganean Hills, a group of volcanic hills that offer a unique landscape. The area is known for its vineyards, thermal springs, and rich biodiversity. Conservation efforts focus on preserving the natural habitats and promoting sustainable agriculture and tourism. The reserve also highlights the region’s cultural heritage, including historic villas and castles.
6. Julian Alps Transboundary Biosphere Reserve (Italy, Slovenia)
The Julian Alps Transboundary Biosphere Reserve straddles the border between Italy and Slovenia. This mountainous region is characterized by its stunning alpine landscapes, diverse flora and fauna, and important cultural sites. The reserve promotes cross-border cooperation in conservation and sustainable development. Efforts include habitat protection, sustainable tourism, and preservation of traditional practices.
7. Khar Us Lake Biosphere Reserve (Mongolia)
Khar Us Lake Biosphere Reserve, located in western Mongolia, is centered around one of the largest freshwater lakes in the country. The area includes wetlands, steppes, and desert landscapes. It is an important habitat for migratory birds and other wildlife. Conservation initiatives focus on water resource management, protecting biodiversity, and supporting sustainable livelihoods for local nomadic communities.
8. Apayaos Biosphere Reserve (Philippines)
The Apayaos Biosphere Reserve in the Philippines is known for its mountainous terrain and diverse ecosystems, including tropical forests and river systems. This area is home to various endemic species and indigenous communities. The reserve’s management strategies emphasize biodiversity conservation, sustainable agriculture, and eco-tourism. Efforts also include preserving the cultural heritage and traditional knowledge of the indigenous people.
9. Changnyeong Biosphere Reserve (Republic of Korea)
The Changnyeong Biosphere Reserve is located in the southern part of the Republic of Korea. It includes a variety of landscapes such as mountains, forests, and wetlands. The area is known for its biodiversity, including rare plant and animal species. Conservation efforts focus on habitat restoration, sustainable land use, and community involvement in environmental protection.
10. Val d’Aran Biosphere Reserve (Spain)
Val d’Aran Biosphere Reserve is situated in the Pyrenees mountains of northeastern Spain. This region is characterized by its alpine landscapes, rich biodiversity, and cultural heritage. The reserve promotes sustainable tourism, conservation of natural habitats, and preservation of traditional agricultural practices. Local communities play a crucial role in managing the reserve and maintaining its unique cultural identity.
11. Irati Biosphere Reserve (Spain)
The Irati Biosphere Reserve, also in Spain, is known for its extensive beech and fir forests, one of the largest and best-preserved in Europe. The area includes diverse habitats that support a variety of wildlife. Conservation efforts focus on maintaining the forest ecosystems, promoting sustainable forestry, and encouraging eco-tourism. The reserve also highlights the cultural and historical significance of the region.
The Importance of Biosphere Reserves
UNESCO Designates 11 New Biosphere Reserves and Biosphere reserves play a critical role in conserving biodiversity. They provide a model for sustainable development. By balancing human activities with nature, these areas ensure long-term ecological health. Here are some key benefits of biosphere reserves:
1. Biodiversity Conservation
Biosphere reserves protect diverse species and habitats. They serve as a refuge for endangered species. By maintaining genetic diversity, they support ecosystem resilience.
2. Sustainable Development
These reserves promote sustainable practices. They encourage eco-friendly agriculture, tourism, and resource management. Local communities benefit from sustainable livelihoods.
3. Research and Education
Biosphere reserves are important sites for scientific research. They provide data on ecological processes and human impacts. Educational programs raise awareness about conservation and sustainability.
4. Climate Change Mitigation
Healthy ecosystems in biosphere reserves can mitigate climate change. Forests and wetlands act as carbon sinks. They absorb carbon dioxide and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Challenges Faced by Biosphere Reserves
UNESCO Designates 11 New Biosphere Reserves and Despite their benefits, biosphere reserves face several challenges. Effective management and community involvement are crucial for their success. Here are some common challenges:
1. Habitat Destruction
Human activities like deforestation, mining, and urbanization can destroy habitats. This leads to the loss of biodiversity. Biosphere reserves need strict regulations to prevent habitat destruction.
2. Climate Change
Climate change affects ecosystems and species. Rising temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events pose threats. Biosphere reserves must adapt to these changes and develop resilience strategies.
3. Resource Overuse
Over-extraction of resources like water, timber, and minerals can degrade ecosystems. Sustainable resource management practices are essential to prevent overuse.
4. Community Engagement
Local communities play a vital role in the success of biosphere reserves. Ensuring their participation and support is crucial. Education and awareness programs can help communities understand the importance of conservation.
The Role of UNESCO
UNESCO Designates 11 New Biosphere Reserves and UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere (MAB) program is instrumental in establishing biosphere reserves. The program promotes international cooperation and knowledge exchange. Here are some key functions of UNESCO in this context:
1. Designation and Recognition
UNESCO designates and recognizes biosphere reserves. This status brings international recognition and support. It also encourages governments and organizations to invest in conservation.
2. Guidelines and Frameworks
UNESCO provides guidelines and frameworks for managing biosphere reserves. These include best practices for conservation, sustainable development, and community engagement.
3. Networking and Collaboration
The MAB program facilitates networking and collaboration among biosphere reserves. It organizes workshops, conferences, and training programs. This helps share knowledge and experiences.
4. Monitoring and Evaluation
UNESCO monitors and evaluates the performance of biosphere reserves. It assesses their effectiveness in achieving conservation and development goals. This ensures accountability and continuous improvement.
Case Studies of Successful Biosphere Reserves
As we know, UNESCO Designates 11 New Biosphere Reserves and Several biosphere reserves around the world have achieved remarkable success. Here are a few examples:
1. Yellowstone Biosphere Reserve (USA)
Yellowstone is one of the oldest and most famous biosphere reserves. It includes the Yellowstone National Park and surrounding areas. The reserve is known for its geothermal features, diverse wildlife, and natural beauty. Successful conservation efforts have led to the recovery of species like the gray wolf and grizzly bear.
2. Great Barrier Reef Biosphere Reserve (Australia)
The Great Barrier Reef is the world’s largest coral reef system. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and biosphere reserve. The area is renowned for its marine biodiversity. Conservation efforts focus on protecting coral reefs from climate change and pollution.
3. Sian Ka’an Biosphere Reserve (Mexico)
Sian Ka’an is located on the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico. It includes tropical forests, wetlands, and coastal ecosystems. The reserve is home to diverse wildlife and Mayan archaeological sites. Conservation efforts promote sustainable tourism and community-based resource management.
4. Vhembe Biosphere Reserve (South Africa)
As one of the new biosphere reserves, Vhembe is already showing promise. Local communities are actively involved in conservation and sustainable livelihoods. The reserve promotes eco-tourism and traditional knowledge.
Biosphere Reserves in India
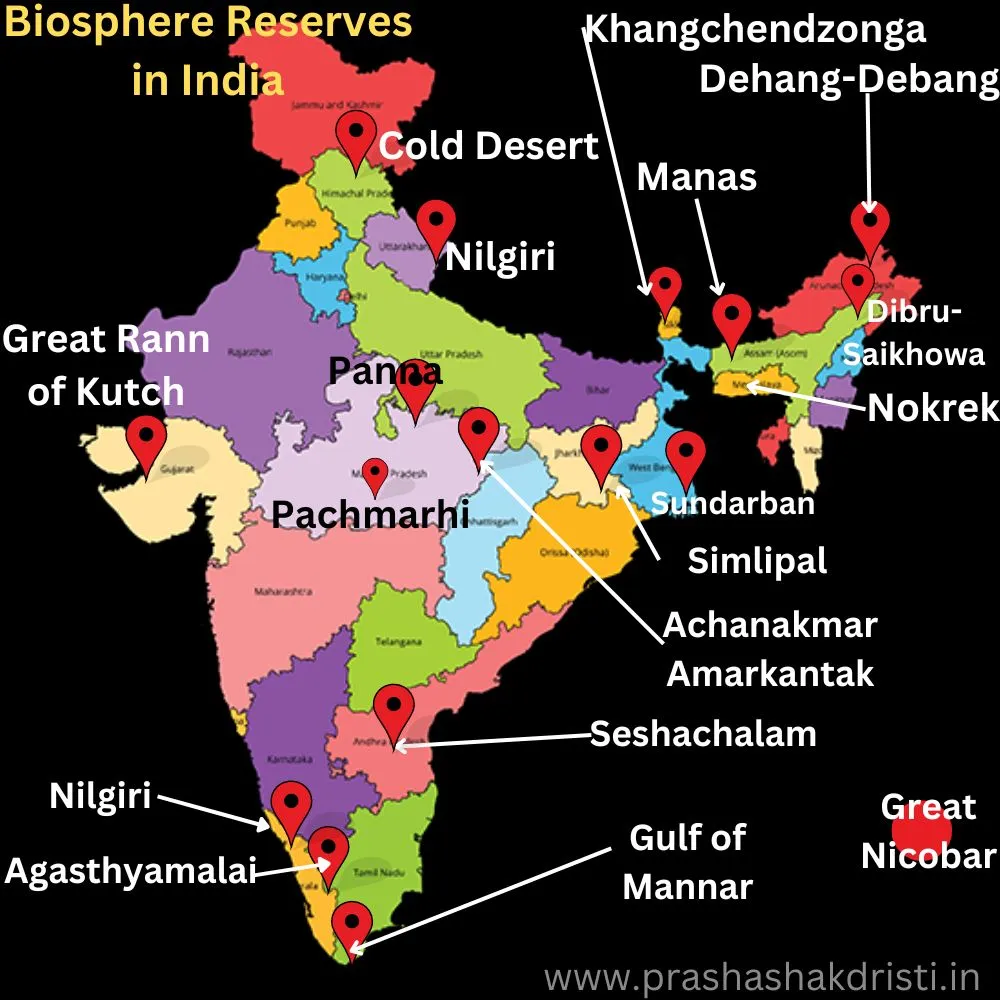
You can read more about – Biosphere Reserves in India-2024
Conclusion
The designation of 11 new biosphere reserves by UNESCO is a significant step towards global conservation. These areas serve as models for balancing conservation with sustainable development. By protecting biodiversity and promoting eco-friendly practices, biosphere reserves ensure a healthy planet for future generations.
Biosphere reserves face challenges like habitat destruction, climate change, and resource overuse. However, with effective management and community engagement, they can overcome these challenges. UNESCO’s MAB program plays a crucial role in supporting and guiding these efforts.
UNESCO Designates 11 New Biosphere Reserves offer opportunities for research, education, and sustainable livelihoods. They contribute to global efforts to mitigate climate change and protect natural resources. By recognizing and supporting these areas, we can build a sustainable future for all.
Q.1 Which biosphere reserve spans the border between Belgium and the Kingdom of the Netherlands?
a) Niumi Biosphere Reserve
b) Colli Euganei Biosphere Reserve
c) Kempen-Broek Transboundary Biosphere Reserve
d) Julian Alps Transboundary Biosphere Reserve
Ans. c) Kempen-Broek Transboundary Biosphere Reserve
Q.2 Which biosphere reserve is located in the northwestern part of Colombia?
a) Darién Norte Chocoano Biosphere Reserve
b) Madre de las Aguas Biosphere Reserve
c) Khar Us Lake Biosphere Reserve
d) Apayaos Biosphere Reserve
Ans. a) Darién Norte Chocoano Biosphere Reserve
Q.3 The Madre de las Aguas Biosphere Reserve is known for its:
a) Coastal mangroves
b) Volcanic hills
c) Mountainous terrain and diverse ecosystems
d) Desert landscapes
Ans. c) Mountainous terrain and diverse ecosystems
Q.4 Which biosphere reserve includes coastal mangroves, wetlands, and savannahs in Gambia?
a) Irati Biosphere Reserve
b) Val d’Aran Biosphere Reserve
c) Niumi Biosphere Reserve
d) Colli Euganei Biosphere Reserve
Ans. c) Niumi Biosphere Reserve
Q.5 The Colli Euganei Biosphere Reserve is located in which region of Italy?
a) Veneto
b) Lombardy
c) Tuscany
d) Sicily
Ans. a) Veneto
Q.6 Which biosphere reserve is a transboundary reserve between Italy and Slovenia?
a) Khar Us Lake Biosphere Reserve
b) Julian Alps Transboundary Biosphere Reserve
c) Changnyeong Biosphere Reserve
d) Kempen-Broek Transboundary Biosphere Reserve
Ans. b) Julian Alps Transboundary Biosphere Reserve
Q.7 Khar Us Lake Biosphere Reserve is centered around one of the largest freshwater lakes in:
a) China
b) Mongolia
c) India
d) Philippines
Ans. b) Mongolia
Q.8 The Apayaos Biosphere Reserve is known for its mountainous terrain and is located in:
a) Philippines
b) Korea
c) Colombia
d) Italy
Ans. Philippines
Q.9 Which biosphere reserve is located in the southern part of the Republic of Korea?
a) Val d’Aran Biosphere Reserve
b) Changnyeong Biosphere Reserve
c) Niumi Biosphere Reserve
d) Irati Biosphere Reserve
Ans. b) Changnyeong Biosphere Reserve
Q.10 The Val d’Aran Biosphere Reserve is situated in which mountain range?
a) Alps
b) Andes
c) Rockies
d) Pyrenees
Ans. Pyrenees
Q.11 The Irati Biosphere Reserve in Spain is known for its extensive:
a) Coastal ecosystems
b) Beech and fir forests
c) Desert landscapes
d) Wetlands
Ans. b) Beech and fir forests

