The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is a significant initiative by the Government of India aimed at promoting financial inclusion across the country. It was introduced on August 28, 2014, with the aim to provide affordable access to financial services like banking, savings, and insurance to every household in the country. This initiative marked a significant step towards bringing the unbanked population into the formal banking system, thereby empowering them economically and socially.
Why was Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana needed?| PMJDY

Before PMJDY, a large section of India’s population, especially in rural areas, lacked access to basic financial services. Many people relied on informal channels for their financial needs, which were often unreliable and costly. The absence of a formal banking structure made it difficult for them to save money safely, access credit, or get insurance coverage. This created a vicious cycle of poverty and economic vulnerability.
The government recognized this gap and launched PMJDY to bridge it. The mission was to ensure that every household had at least one bank account, which would serve as a foundation for them to avail other financial services.
There are near about 53 crore Benificiary comes under this scheme.
Key Objectives of PMJDY
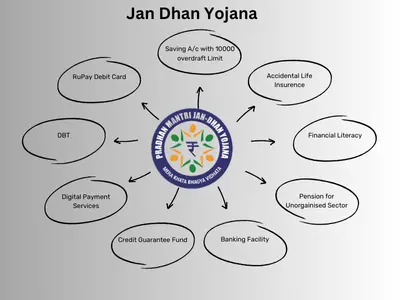
- Universal Banking Access: The primary objective of PMJDY is to provide universal access to banking facilities, particularly in rural areas. This includes opening bank accounts, providing debit cards, and offering mobile banking services.
- Financial Literacy: The scheme also aims to promote financial literacy among the economically weaker sections. Educating people about managing their finances, the benefits of saving, and the importance of insurance is crucial for their financial well-being.
- Insurance and Pension: PMJDY offers life insurance and accidental insurance coverage to account holders. It also provides access to government pension schemes, which are vital for ensuring financial security in old age.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): One of the significant benefits of having a bank account under PMJDY is the direct transfer of government subsidies and benefits. This eliminates the need for middlemen and ensures that the money reaches the rightful beneficiaries.
Salient Features of PMJDY
- Zero Balance Account: One of the most attractive features of the Jan Dhan accounts is that they can be opened with zero balance. This makes it accessible to even the poorest of the poor, who might not have the initial deposit required by traditional bank accounts.
- RuPay Debit Card: Every Jan Dhan account holder receives a RuPay debit card. This card can be used for cash withdrawals, online transactions, and even for purchasing goods at merchant outlets.
- Overdraft Facility: After six months of satisfactory operation of the Jan Dhan account, the account holder becomes eligible for an overdraft facility. This provides them with emergency credit of up to ₹10,000, which can be a lifeline during financial crises.
- Accident Insurance Cover: Jan Dhan account holders are entitled to an accidental insurance cover of up to ₹2 lakh. This insurance is linked to the RuPay debit card provided under the scheme.
- Life Insurance Cover: Along with accident insurance, the scheme also offers a life insurance cover of ₹30,000 to the account holders who open their accounts within the first 15 days of the scheme’s launch.
- Mobile Banking Facility: PMJDY accounts come with basic mobile banking facilities. This enables account holders to check their balance, transfer funds, and even pay bills through their mobile phones, making banking more accessible.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): The government transfers subsidies directly to the Jan Dhan accounts under the DBT scheme. This includes subsidies for LPG, kerosene, and other government schemes, ensuring transparency and reducing leakages.
Achievements of PMJDY
Since its inception, PMJDY has made remarkable strides in achieving its objectives. As of August 2024, more than 53crore accounts have been opened under the scheme, with a significant portion in rural areas. The scheme has not only brought millions of people into the formal banking system but has also empowered them by providing access to various financial services.
- Increased Savings: The scheme has encouraged a culture of saving among the economically weaker sections. The total balance in these accounts has crossed ₹1.5 lakh crore, indicating the success of the initiative in promoting savings.
- Empowerment of Women: PMJDY has played a crucial role in empowering women. A large number of accounts have been opened in the name of women, giving them control over their finances and increasing their participation in the financial system.
- Social Security: The insurance and pension schemes linked with Jan Dhan accounts have provided a safety net to millions of families. This has reduced their vulnerability to economic shocks and ensured financial stability.
- Transparency in Government Schemes: The direct benefit transfer mechanism under PMJDY has brought transparency to the disbursement of government subsidies. It has eliminated corruption and ensured that the benefits reach the intended beneficiaries without any delays.
Challenges Faced by PMJDY
While PMJDY has been successful in many aspects, it has also faced several challenges:
- Dormant Accounts: A significant number of Jan Dhan accounts remain dormant, meaning there have been no transactions in these accounts for a long period. This defeats the purpose of financial inclusion, as the account holders are not actively using the banking services.
- Limited Financial Literacy: Despite efforts to promote financial literacy, many account holders still lack a basic understanding of banking services. This limits their ability to fully utilise the benefits offered by PMJDY.
- Connectivity Issues: In remote areas, poor connectivity and lack of infrastructure hinder the effective implementation of mobile banking services. This makes it difficult for account holders to access their accounts and avail themselves of banking services.
- Overdraft Repayment: The overdraft facility is beneficial, but many account holders struggle to repay the overdraft amount. This creates a risk of bad debts and financial burden on the banks.
Future Prospects of PMJDY
The government continues to strengthen the PMJDY scheme to overcome the challenges and expand its reach. Some of the future prospects include:
- Improving Financial Literacy: The government plans to intensify its efforts in financial literacy programs. This will help account holders better understand banking services and encourage them to use their accounts more actively.
- Technological Advancements: With the rapid advancements in technology, the government aims to enhance the digital infrastructure in rural areas. This will improve connectivity and make mobile banking services more accessible to Jan Dhan account holders.
- Linking with More Government Schemes: The government is considering linking Jan Dhan accounts with more welfare schemes. This will ensure that the benefits of various government programs reach the intended beneficiaries directly.
- Encouraging Active Use of Accounts: To address the issue of dormant accounts, the government is exploring incentives for account holders to actively use their Jan Dhan accounts. This could include benefits like higher interest rates on savings or additional insurance coverage.
Conclusion
The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana has been a game-changer in India’s financial inclusion journey. It has brought millions of people into the formal banking system, providing them with access to essential financial services. While challenges remain, the government’s continued efforts to strengthen the scheme and promote financial literacy will ensure its long-term success. PMJDY is not just a scheme; it is a mission to empower every citizen with financial security and dignity. The success of this mission will pave the way for a more inclusive and economically stable India.
You can read more article here – Unified Pension Scheme
FAQs
What is Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)?
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana is a financial inclusion initiative launched by the Government of India on August 28, 2014. The scheme aims to provide universal access to banking facilities, ensuring that every household in India has at least one bank account.
Who is eligible to open a Jan Dhan account (PMJDY)?
Any Indian citizen above the age of 10 years can open a Jan Dhan account. There are no specific income criteria for eligibility, making it accessible to everyone, including those in rural and urban areas.
What documents are required to open a Jan Dhan account?
The basic documents required include proof of identity and proof of address. The Aadhaar card can be used as both identity and address proof. In cases where Aadhaar is not available, a voter ID card, PAN card, passport, or driving licence can be used.
Is there a minimum balance requirement for Jan Dhan accounts?
No, Jan Dhan accounts can be opened with zero balance. However, if the account holder wants to avail of the cheque book facility, they may need to maintain a minimum balance as per the bank’s guidelines.
What benefits do Jan Dhan account holders receive?
Jan Dhan account holders receive several benefits, including a RuPay debit card, accidental insurance cover of ₹2 lakh, life insurance cover of ₹30,000, access to overdraft facilities, and the ability to receive government subsidies directly into their account through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
What is the overdraft facility in a Jan Dhan account?
The overdraft facility allows Jan Dhan account RuPay Card holders to borrow a small amount of money (up to ₹10,000) from the bank, even if their account balance is zero. This facility is available after six months of satisfactory operation of the account.
Can I convert my existing savings account into a Jan Dhan account?
Yes, an existing savings account can be converted into a Jan Dhan account. You need to visit your bank branch and request the conversion. After conversion, you will be eligible for all the benefits provided under the PMJDY scheme.
How can I check the balance in my Jan Dhan account?
The balance in a Jan Dhan account can be checked using various methods, including visiting the bank branch, using an ATM, checking via mobile banking, or using internet banking services.
Is there any charge for maintaining a Jan Dhan account?
No, there is no charge for maintaining a Jan Dhan account. The account can be maintained with zero balance, and the account holder does not need to pay any fees for basic banking services.
What happens if a Jan Dhan account remains inactive?
If a Jan Dhan account remains inactive for a long period, it may be classified as dormant. The account holder will need to perform a transaction, such as depositing or withdrawing money, to reactivate the account.
Are there any special benefits for women under PMJDY?
Yes, a large number of Jan Dhan accounts have been opened in the name of women, empowering them financially. The government encourages women to open these accounts to increase their financial independence and participation in the economy.
Can I use my Jan Dhan account for receiving government subsidies?
Yes, one of the primary purposes of the Jan Dhan account is to facilitate the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) of government subsidies directly into the beneficiary’s account, ensuring transparency and eliminating middlemen.

