Biosphere Reserves in India play a very important role to conserve nature. India is a land of rich biodiversity. It has many unique ecosystems. To protect these, India has set up biosphere reserves. These reserves aim to conserve wildlife and promote research and education. Let’s explore the importance of biosphere reserves in India.
What are Biosphere Reserves?
Biosphere reserves are areas of terrestrial and coastal ecosystems. They promote the conservation of biodiversity. They also ensure sustainable use of natural resources. These reserves are recognized under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme.
Importance of Biosphere Reserves
- Biodiversity Conservation: They protect various species of plants and animals.
- Research and Education: They offer opportunities for scientific research.
- Sustainable Development: They promote sustainable use of natural resources.
- Cultural Preservation: They help in preserving the cultural heritage of local communities.
How many biosphere reserves in India
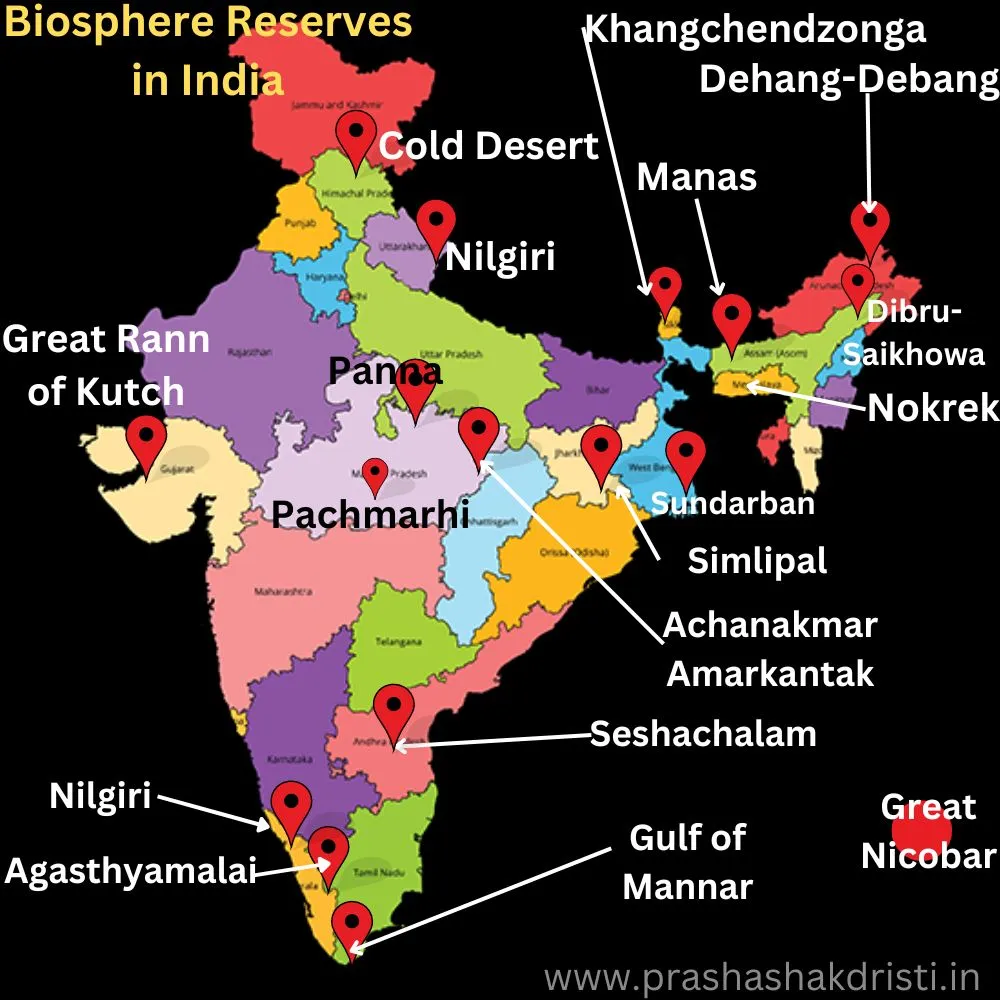
There are 18 biosphere reserves in India some of them are here in detail-
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve is the first biosphere reserve in India. It includes the Nilgiri Hills of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Karnataka. This reserve is known for its rich flora and fauna. Key species include the Nilgiri Tahr, Indian Elephant, and Bengal Tiger. It also hosts several tribal communities who have lived in harmony with nature for centuries.
Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve
Sundarbans is famous for its mangrove forests and the Royal Bengal Tiger. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The reserve is located in the delta region of Padma, Meghna, and Brahmaputra river basins. It is also home to a variety of bird species, reptiles, and invertebrate species.
Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve
Gulf of Mannar is one of the richest coastal regions in India. It has coral reefs, seagrass beds, and mangroves. This reserve is crucial for the conservation of marine biodiversity. It is home to several endangered species like the dugong and the green sea turtle.
Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve
Located in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, this reserve is known for its unique tropical rainforest. It is home to the indigenous Nicobarese and Shompen tribes. The reserve is also rich in marine life, including coral reefs and sea turtles.
Simlipal Biosphere Reserve
Simlipal in Odisha is a vital biosphere reserve. It is a tiger reserve and an elephant reserve. The area is rich in biodiversity, with numerous species of plants, animals, and birds. The tribal communities living here depend on the forest for their livelihood.
Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve
This reserve is named after the Agasthyamalai Hills. It spans across Tamil Nadu and Kerala. The reserve is known for its medicinal plants and diverse flora and fauna. It is also home to several tribal communities who rely on the forest resources.
Challenges Facing Biosphere Reserves
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation and land use changes threaten these reserves.
- Poaching and Illegal Trade: Wildlife poaching and illegal trade of species are major concerns.
- Climate Change: Changes in climate patterns impact biodiversity.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Encroachment by humans leads to conflicts with wildlife.
- Pollution: Pollution of air, water, and soil affects the health of ecosystems.
Conservation Efforts
- Strict Regulations: Enforcing strict laws to prevent poaching and illegal activities.
- Community Involvement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts.
- Research and Monitoring: Continuous research and monitoring of biodiversity.
- Eco-tourism: Promoting eco-tourism to create awareness and generate funds for conservation.
- Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable agricultural and forestry practices.
List of Biosphere Reserves in India
| SR | Biosphere Reserve | Establishment Year | Area (sq km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve | 1986 | 5,520 |
| 2 | Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve | 1988 | 5,860 |
| 3 | Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve | 1989 | 9,630 |
| 4 | Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve | 1989 | 10,500 |
| 5 | Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve | 1989 | 885 |
| 6 | Manas Biosphere Reserve | 1989 | 2,837 |
| 7 | Simlipal Biosphere Reserve | 1994 | 4,374 |
| 8 | Dibru-Saikhowa Biosphere Reserve | 1997 | 765 |
| 9 | Dehang-Debang Biosphere Reserve | 1998 | 5,112 |
| 10 | Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve | 1999 | 4,926 |
| 11 | Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve | 2000 | 2,619 |
| 12 | Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve | 2001 | 1,828 |
| 13 | Achanakmar-Amarkantak Biosphere Reserve | 2005 | 3,835 |
| 14 | Kachchh Biosphere Reserve | 2008 | 12,454 |
| 15 | Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve | 2009 | 7,770 |
| 16 | Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve | 2010 | 4,755 |
| 17 | Panna Biosphere Reserve | 2011 | 2,998 |
| 18 | Sundarban Biosphere Reserve | 2013 | 9,630 |
Largest Biosphere Reserves in India
Here is the list of Largest Biosphere Reserves in India-
Here is the corrected and complete table with 19 biosphere reserves of India, arranged in increasing order of area:
| SR | Biosphere Reserve | Area (sq km) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dibru-Saikhowa Biosphere Reserve | 765 |
| 2 | Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve | 885 |
| 3 | Agasthyamalai Biosphere Reserve | 1,828 |
| 4 | Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve | 2,619 |
| 5 | Manas Biosphere Reserve | 2,837 |
| 6 | Panna Biosphere Reserve | 2,998 |
| 7 | Achanakmar-Amarkantak Biosphere Reserve | 3,835 |
| 8 | Simlipal Biosphere Reserve | 4,374 |
| 9 | Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve | 4,755 |
| 10 | Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve | 4,926 |
| 11 | Dehang-Debang Biosphere Reserve | 5,112 |
| 12 | Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve | 5,520 |
| 13 | Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve | 5,860 |
| 14 | Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve | 7,770 |
| 15 | Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve | 9,630 |
| 16 | Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve | 10,500 |
| 17 | Kachchh Biosphere Reserve | 12,454 |
| 18 | Dihang-Dibang Biosphere Reserve | 5,112 |
Map of Biosphere Reserves in India
Conclusion
Biosphere reserves in India play a crucial role in conserving biodiversity. They provide a balance between nature conservation and sustainable use of resources. It is essential to continue efforts in preserving these vital areas. With proper management and community involvement, biosphere reserves can thrive and benefit future generations.
India’s biosphere reserves are a testament to its commitment to protecting the environment. They are a treasure trove of natural wealth and cultural heritage. By understanding and supporting these reserves, we can contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
You can also read about – Farmer Registry Scheme: 2024

